Force Calculator for Shaker Systems
Estimate required shaker force for:
- Random (Grms → NRMS)
- Sine (peak or RMS)
- Max Mass (Total moving mass = DUT + armature + fixturing)
Why Force doesn’t tell the full story
If you’re trying to size a shaker or determine if your existing shaker can perform a given test profile, force is an important element but not the only one to be considered. Let’s first look at how force is calculated in the above calculator:
F = MA (force = mass x acceleration)
This is a calculation and represents theoretical values. In other words, shaker systems have physical limitations. This calculation is a starting point and must be checked against the shaker specifications. As an example a shaker system with 10,000 lbf force rating will calculate a 200g sine test with a 50 lb test item. In reality that shaker system might have a 100g limit to prevent damage to itself. Conversely the same shaker will calculate a 0.1g sine test with a 100,000 lb test item, but the shaker system might have a test mass limitation of 2,000 lbs. I think you get the point.
You’ll have to also consider these elements of a shaker system:
- Displacement (p-p)
- Velocity (p)
Let’s examine each one further:
Displacement – also known as stroke, this is the maximum movement range of the shaker armature. Normally presented in peak-to-peak (if only peak, double the value to get peak-to-peak), this will be in mm or inches units. Most vibration test profiles have the greatest displacement requirement in the lower frequencies. As an example the p-p displacement needed for 1g at 1Hz is 19.56 inches. Whereas 1g at 5Hz is 0.7824 inches.
Velocity -Velocity is the change in displacement (distance traveled) over time. It’s essentially the speed of something. Shaker systems have a limit on how fast the armature can move based on the displacement rating of the shaker and frequency. As an example the velocity requirements for 1 inch p-p displacement at 1Hz is 3.14 inches/sec. Whereas 1 inch p-p displacement at 5Hz is 15.71 inches/sec. The velocity limitation of a shaker system is usually found in-between the maximum displacement (low frequency) and maximum acceleration limits (higher frequency).
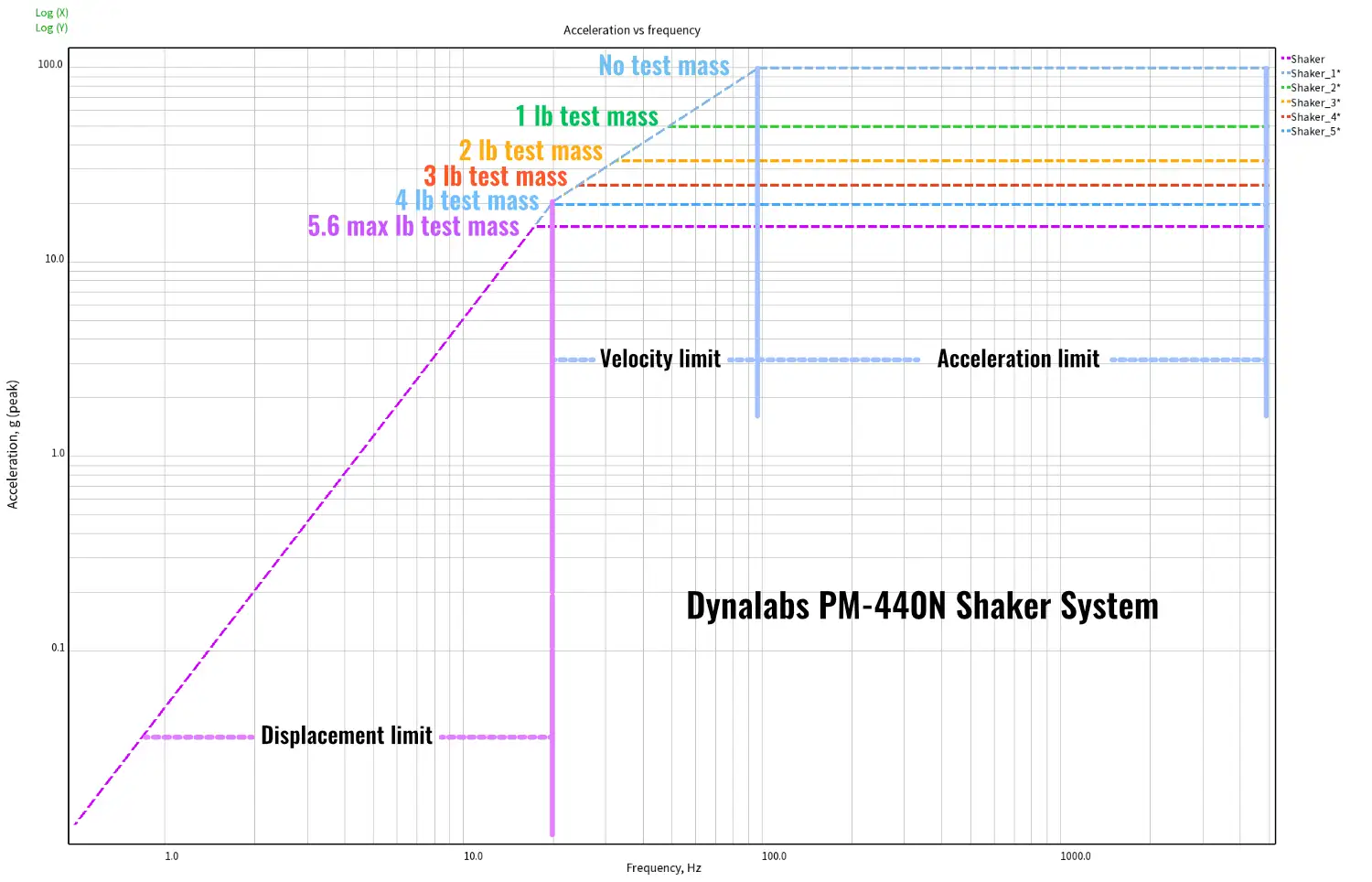
Sine Performance Curve
A sine performance curve is shaker-system-specific graphical spec sheet. It allows users to see the acceleration, velocity and displacement limits of a given shaker system with a range of test masses (including no test mass representing the full capability of that shaker, but includes the armature mass). The full force capability is shown by the maximum acceleration level for the different masses. As we increase test mass the maximum acceleration is reduced. All test masses follow the displacement and velocity curve until it hits it’s maximum acceleration level. Here is an example of a sine performance curve for a Dynalabs PM-440 shaker system.
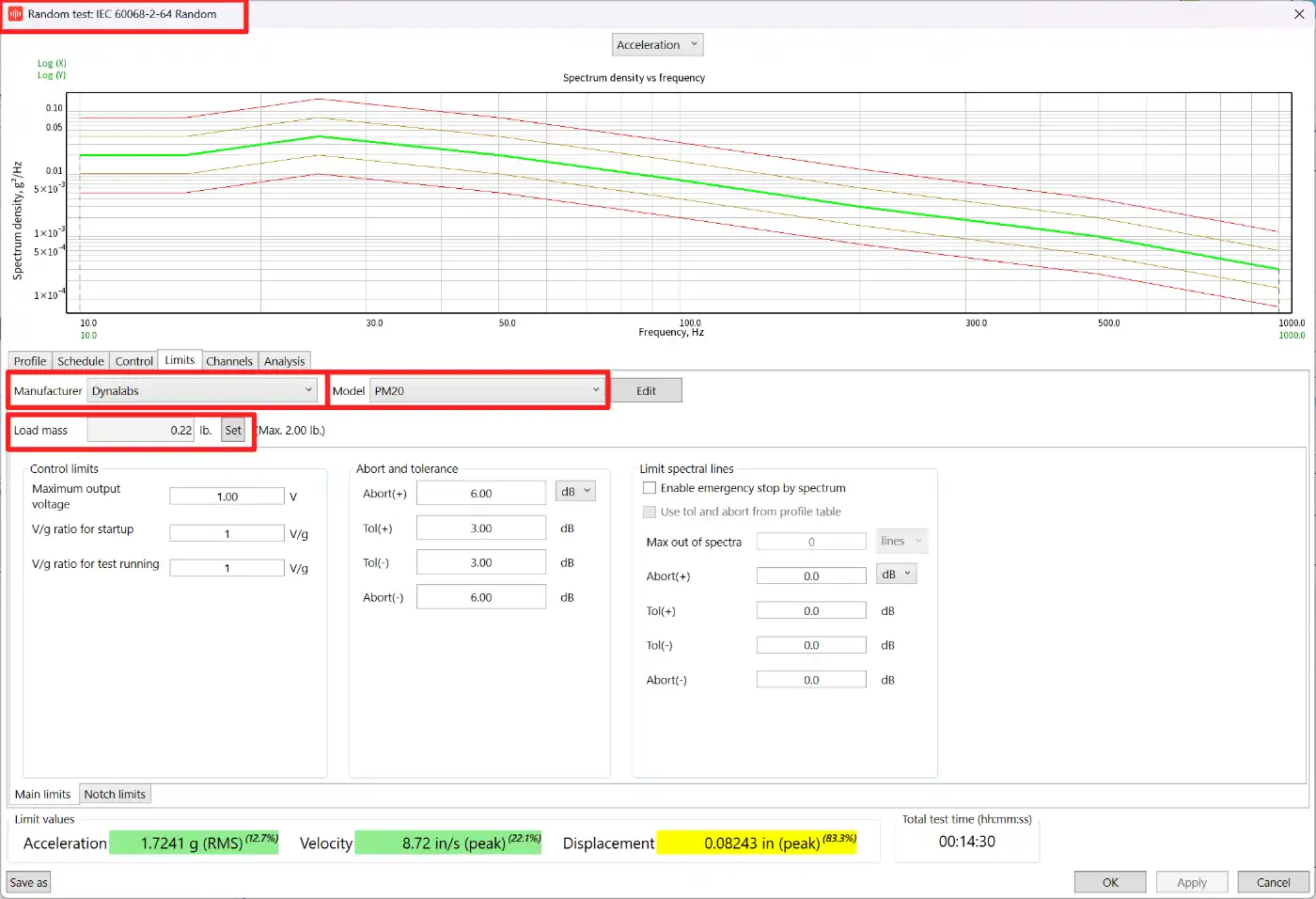
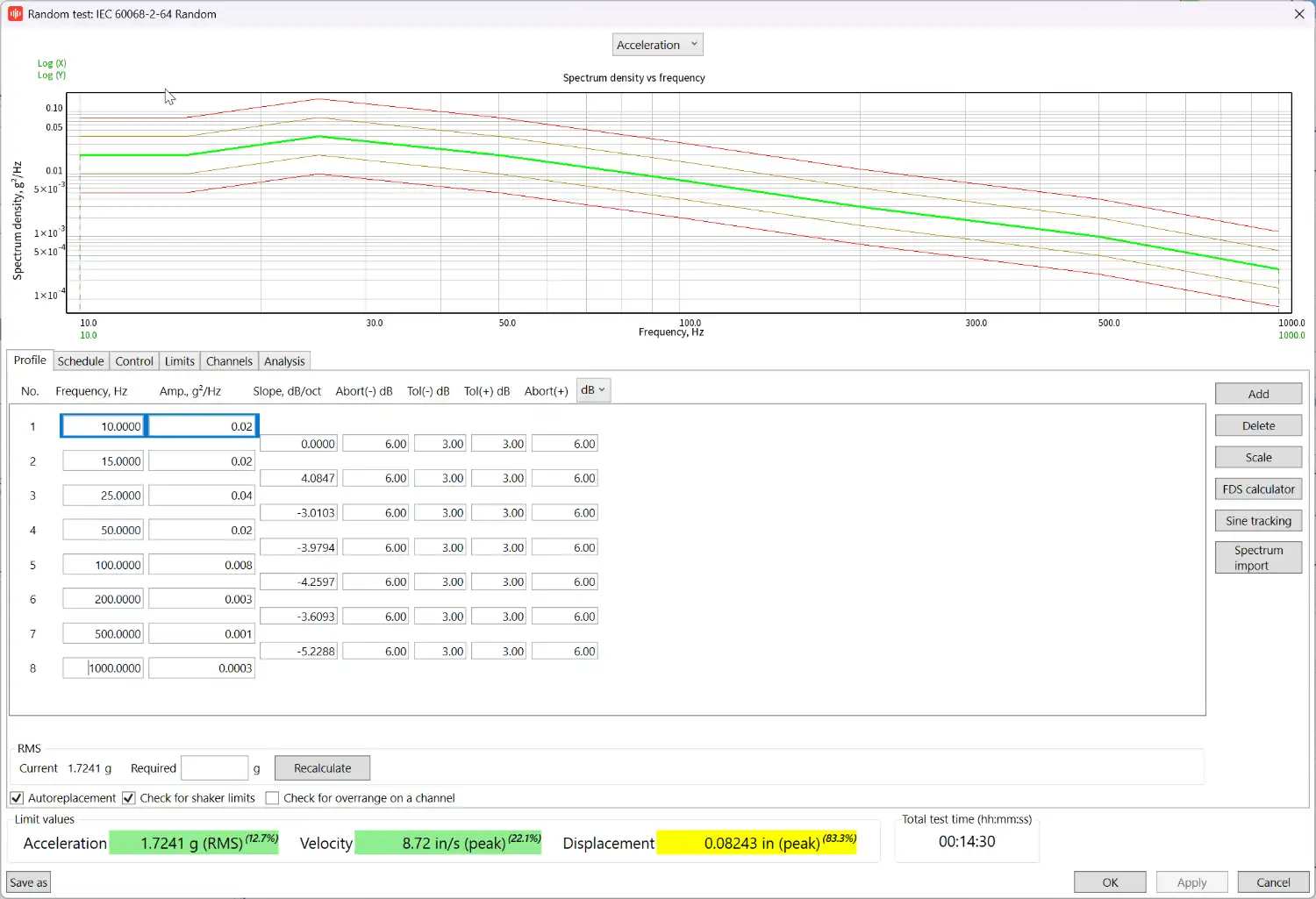
Calculate force, acceleration, velocity & Displacement
Download RULA Technologies TestUP software to calculate the force, acceleration, velocity and displacement needed for a particular vibration test profile. Select your test type, shaker, test mass and enter the test profile details. The software will calculate the required acceleration, velocity and displacement requirements, and based on the selected shaker system let you know if you’re within the shaker limits. The maximum force is calculated using the test mass vs acceleration values.
This is a free tool. Click the link below to register and download TestUP software today!
Select/enter your shaker details

Select test type and enter test mass